Ectopic Pregnancy
Symptoms of Ectopic Pregnancy
Symptoms of ectopic pregnancy usually appear early in pregnancy (weeks 6 to 10) and include:
- Severe pelvic or abdominal pain: The pain may be intense, continuous, or intermittent and can radiate to the shoulder or neck.
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding: Light or heavy bleeding that differs from regular menstrual bleeding.
- Dizziness or weakness: Caused by low blood pressure due to internal bleeding.
- Rapid or weak heartbeat: This may be a sign of shock caused by severe bleeding.
Diagnosis of Ectopic Pregnancy
The diagnosis of ectopic pregnancy is typically made through a combination of clinical exams, blood tests, and imaging:
- Blood test: Measurement of HCG (human chorionic gonadotropin) levels in the blood; abnormal levels of this hormone can indicate ectopic pregnancy.
- Transvaginal ultrasound: An ultrasound through the vagina to visualize the pelvis and identify the location of the fertilized egg.
- Pelvic exam: To assess for pain, swelling, or tenderness in the pelvic area.
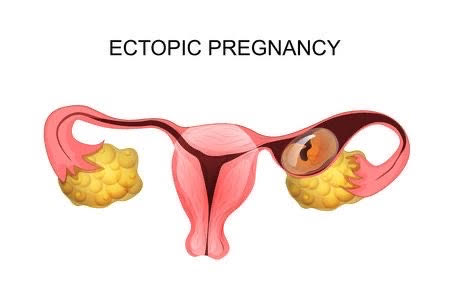
An ectopic pregnancy, or extrauterine pregnancy, occurs when a fertilized egg implants outside the uterus, usually in one of the fallopian tubes. This type of pregnancy cannot develop normally and requires immediate medical intervention, as it poses serious health risks for the mother.
Causes of Ectopic Pregnancy
Damage or blockage of the fallopian tubes: Damage to the fallopian tubes from pelvic infections, previous surgeries, or pelvic inflammatory disease (PID) can lead to ectopic pregnancy.
- Hormonal factors: Hormonal changes can affect the movement of the fertilized egg within the fallopian tubes.
- Structural abnormalities: Congenital anomalies or damage from previous surgeries may alter the pathway of the fallopian tubes, leading to ectopic pregnancy.
- Medications or fertility treatments: Hormonal medications to stimulate ovulation or the use of assisted reproductive techniques (ART) can increase the risk of ectopic pregnancy.

Treatment of Ectopic Pregnancy
Treatment of ectopic pregnancy depends on the location and stage of the pregnancy, the mother’s overall health, and present symptoms. Treatment options include:
- Medication: This method is typically used in the early stages of pregnancy when there is no risk of fallopian tube rupture.
- Laparoscopic surgery: A minimally invasive procedure to remove the fertilized egg and repair the damaged fallopian tube. This method is preferred as it involves smaller incisions and faster recovery.
- Open surgery (laparotomy): In more complex cases or when there is severe bleeding, open surgery is performed.
- Monitoring and follow-up: In some cases, where the ectopic pregnancy resolves on its own, the physician may opt for close monitoring and regular follow-ups with the patient.
